Virtualization is one of concepts that has been on the rise in the recent years
as it makes the lives of developers and people managing company infrastructure a lot easier.
In this Article, we will take a look at,
- Fundamentals of Virtualization
- What are Hypervisors
- Various Types of Virtualization
- And Finally, the Benefits of using Virtualization
that exists in the context of computers and information technology.
So, without further ado, let’s get started!

The Fundamentals of Virtualization
Virtualization at it’s core is taking a piece or multiple pieces of Physical Hardware, Service, Data, etc like
- Processors
- RAM
- Storage Devices – Hard Disk, Solid State Drives, NVMe SSDs
- Network Resources
- or other Server Resources
and converting it by consolidating or dividing it into a single or multiple virtual pieces of the same
in a way that it will be detected, managed and used as an independent piece of Physical Hardware, Service, Data, etc.
The way Virtualization works practically is that,
instead of having a single environment having total control of all the Physical Resources
we create a layer of abstraction that that sits between the said environment and Physical Resources
which will manage – How the Physical Resources will be given to the said environment.
This layer of abstraction will allow us to run
Multiple Virtual Environments / Operating Systems in Parallel on the same Physical Hardware
which would not have been possible before.
So basically, if you suppose had 1 TB of Storage Space,
then through this layer of abstraction you can divide it up, equally or unequally, however you want
and give them to the n number of Virtual Environments / Operating Systems that you have running.
The Virtual Environments are often also known as Virtual Machines or Guest Machines
and such Virtual or Guest Machine are in almost all cases stored a Single File in your Storage Device
making it really easy to take your Virtual Environments / Virtual Machine with you wherever you want.
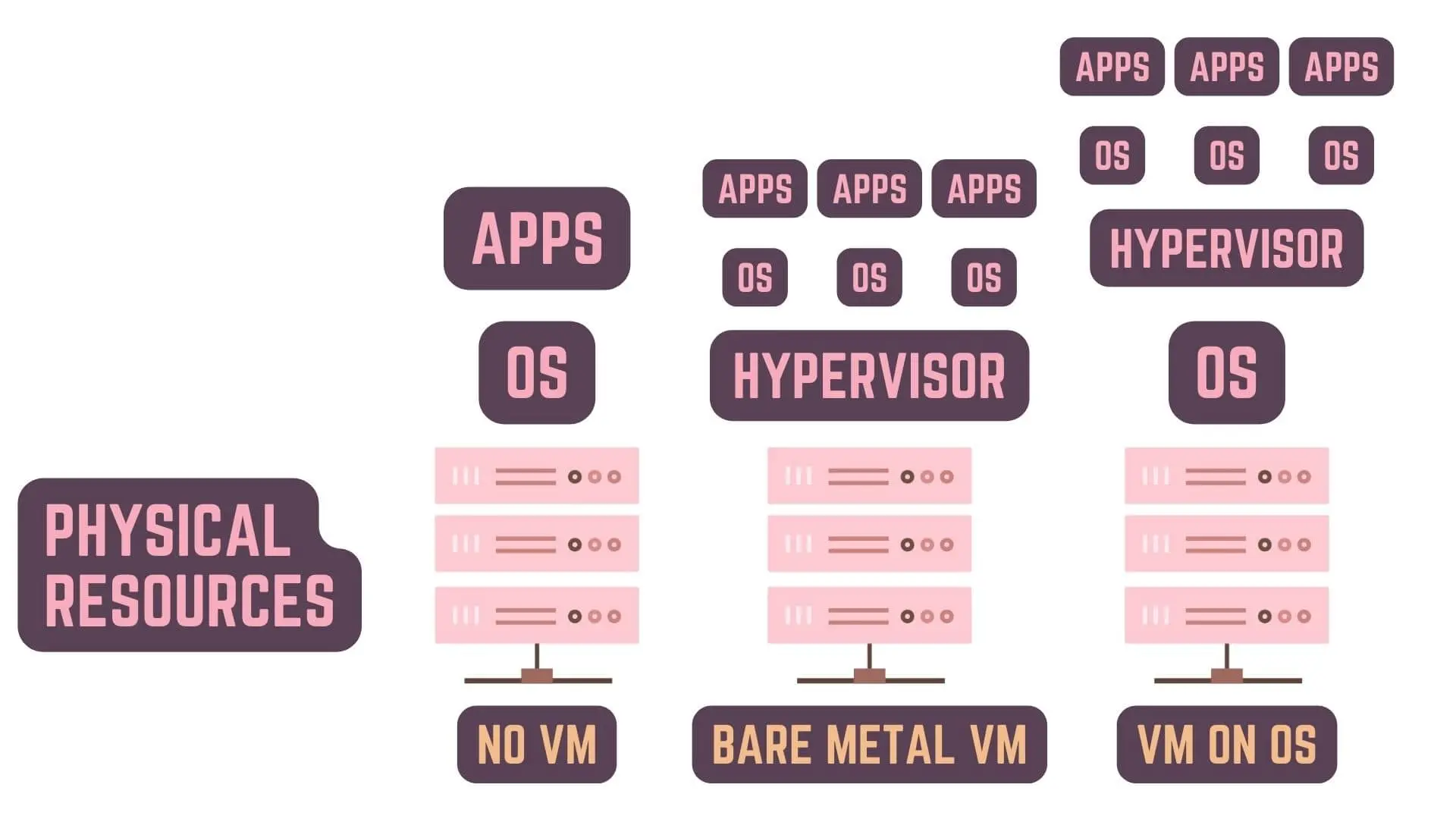
What are Hypervisors
So, the abstraction that sits between the Virtual Machines and the Physical Resources
is a literally just piece of software as I’ve said above
and this software is what we call a Hypervisor.
Hypervisors can run directly on a Bare Metal i.e. Physical Hardware or as an Application on top of another Operating System.
In enterprises or companies, that use such technologies, they usually run Hypervisors directly on Bare Metal
so as to not have the overhead of another Operating System between the Hypervisor and the Physical Resources.
Types Of Virtualization
The list below are the Various Types of Virtualization which can be helpful
based on the type of environments you are trying to create and what problems you are trying to solve.
I won’t be going into detail about them
but i’ll link some resources where you can learn more about each of them.
- Data Virtualization
- Storage Virtualization
- Application Virtualization
- Desktop Virtualization
- Server Virtualization
- Operating System Virtualization
- Network Function Virtualization
Advantages of Virtualization
Now as you will already know, companies usually don’t use something new
which will need them to move their underlying infrastructure
without the new way having some significant benefits.
Virtualization is also the same and it has some pretty significant Advantages like
- Reduces the number of Physical Hardware that the company needs
because now they can virtualize many things which needed Discrete Physical Hardware before. - Lowers Cost of Maintenance of Physical Hardware as the number of Physical Hardware has decreased
and the company doesn’t need to pay for partially utilized hardware because we have virtualized the resources. - Easy Backups and Migration as each Virtual Machine is usually stored on literally just a single file
and that is all you will need to migrate your Virtual Machine. - Easy Testing and Disaster Recovery as Virtual Machines take frequent Snapshots of the Virtual Machine
and if anything goes wrong, while you are developing or testing something,
you can just revert back to the last Snapshot that was taken of your Virtual Machine.
Conclusion
Well Folks! I hope that the information within this article was helpful to you.
Have a Great Day and may you have success in your career, whatever it may be!
Share this post on Social Media platforms, if you think our content is great.
If you like the content and would like to follow us, we are present on the platforms below
Follow Us On Social Media
Goodbye For Now,
This is your host VP
Signing Off.
Articles In WordPress Tutorial For Beginners Series
Develop WordPress Websites locally on your computer using XAMPP Server Stack
Articles In Basics Of Internet Series
Basics Of Websites & How They Work
Basics Of Web Servers | Self Hosted, Shared Hosted, VPS, Dedicated Web Servers
Cloud Hosting Vs Traditional Web Hosting
Articles In Web Development Basics Series
Virtualization, Hypervisors & Virtual Machines (VM)
IP Address and DNS (Domain Name System)
DNS Records | A, AAAA, CNAME, MX, TXT, NS, SOA, SRV, PTR & CAA Records
Articles In Monetizing Websites Series
Understanding Audience Intent Of Your Blog Traffic
Building a Monetization Strategy (Not Uploaded)
Digital Marketing Revenue Models – CPM, CPC, CPA, CPL & CPI
Affiliate Marketing & Monetizing Your Blog Using It. (Not Uploaded)
How is your Ad Inventory Auctioned (Not Uploaded)
Affiliate Marketing and Why it Works. (Not Uploaded)





